Abstract
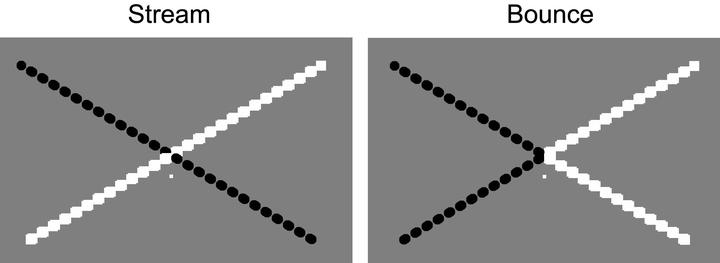
Causality poses explicit constraints to the timing of sensory signals produced by events, as sound travels slower than light, making auditory stimulation to lag visual stimulation. Previous studies show that implied causality between unrelated events can change the tolerance of simultaneity judgments for audiovisual asynchronies. Here, we tested whether apparent causality between audiovisual events may also affect their perceived temporal order. To this aim, we used a disambiguated stream-bounce display, with stimuli either bouncing or streaming upon each other. These two possibilities were accompanied by a sound played around the time of contact between the objects, which could be perceived as causally related to the visual event according to the condition. Participants reported whether the visual contact occurred before or after the sound. Our results show that when the audiovisual stimuli are consistent with a causal interpretation (i.e., the bounce caused the sound), their perceived temporal order is systematically biased. Namely, a stimulus dynamic consistent with a causal relation induces a perceptual delay in the audio component, even if the sound was presented first. We thus conclude that causality can systematically bias the perceived temporal order of events, possibly due to expectations based on the dynamics of events in the real world.