Abstract
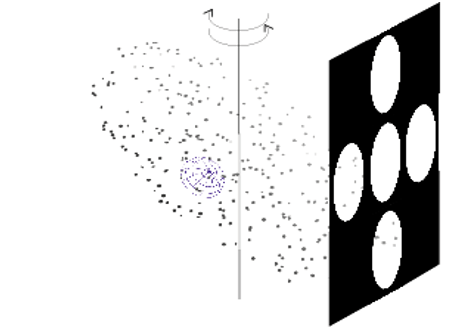
In three experiments we investigated whether the perception of 3D structure from the optic-flow involves a process of spatial integration. The observer’s task was to judge the 3D orientation of local velocity field patches. In two conditions, the patches were presented either in isolation, or as part of a global optic-flow. In Experiment 1, the global optic-flow was a linear velocity field. In Experiment 2, the patches were embedded in a randomly perturbed linear velocity field. In Experiment 3, the local patches belonged to a smoothly curved surface. The results of these three experiments lead to two main conclusions: (1) a process linking spatially separated patches into global entities does affect the perception of local surface orientation induced by the optic-flow, and (2) linearity or smoothness of the global velocity field are not necessary conditions for spatial integration.