Exogenous cueing of visual attention using small, directional, tactile cues applied to the fingertip
Abstract
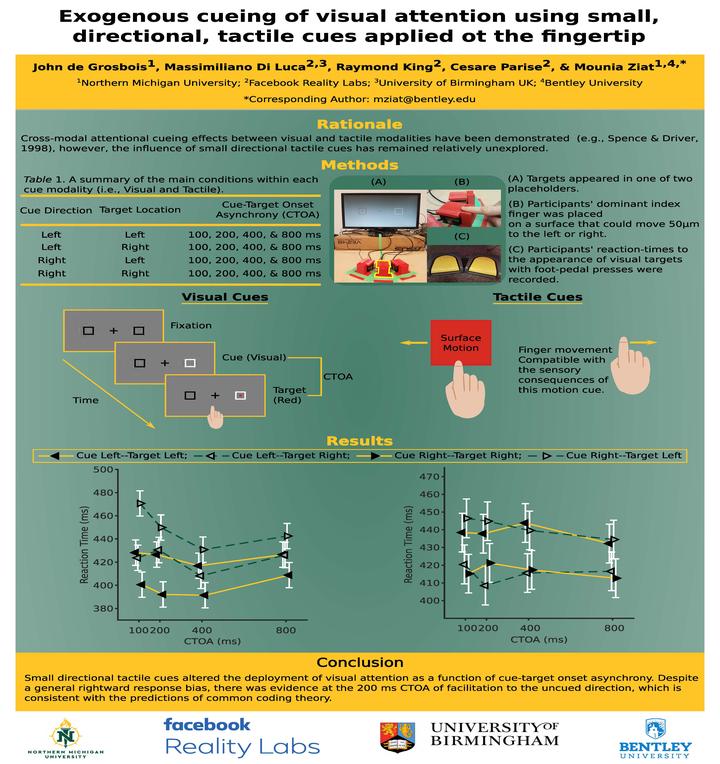
The deployment of visual spatial attention can be significantly influenced in an exogenous, presumably bottom-up manner. Traditionally, spatial cueing paradigms have been utilized to come to such conclusions. Although these paradigms have primarily made use of visual cues, spatially correspondent tactile cues have also been successfully employed. However, one property of tactile cues not thoroughly explored in this context is the influence of their specific directionality on the subsequent deployment of visual attention. Thus, the current study sought to evaluate the potential utility of small, directional tactile cues as a means to exogenously direct visual spatial attention. Tactile cues were employed by a small shearing of the fingertip’s skin in either the leftward of rightward direction. A modified spatial cueing paradigm was used to compare reaction time performance across both traditional-visual and directionaltactile cues at cue-target onset asynchronies of 100, 200, 400 and 800 ms. The results indicated that both visual and tactile cues mediated the deployment of exogenous visual spatial attention. However, differences between the two modalities were observed in terms of both the magnitude and the pattern of the associated cueing effects. Further, there appeared to be a general rightward bias in performance irrespective of cue modality. Overall, the current work offers preliminary evidence that small, directional tactile stimulation may influence the allocation of attention across space in a manner at least partially distinct to traditional visual cueing tasks. Yet, further research will be required to explicitly determine the underlying mechanisms.